Understanding Quota Rent: A Comprehensive Guide
Quota rent is a term often encountered in discussions related to trade, economics, and international agreements. It refers to the economic benefit that arises from the allocation of import or export quotas. This concept plays a significant role in shaping global trade policies and has far-reaching implications for businesses and consumers alike. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of quota rent, exploring its definition, applications, and impact on the global economy.
Quota rent is not just a theoretical concept; it has real-world applications that affect industries and economies around the globe. Understanding this term is crucial for policymakers, economists, and business leaders who aim to navigate the complexities of international trade.
As we explore the concept of quota rent, we will also examine its historical context, the mechanisms through which it operates, and its relevance in contemporary trade discussions. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of quota rent and its significance in shaping global trade dynamics.
Read also:Mastering Remoteiot Vpc Ssh Raspberry Pi A Free Windows Download Guide
Table of Contents
- What is Quota Rent?
- Types of Quotas
- Mechanisms of Quota Rent
- Economic Impact of Quota Rent
- Quota Rent in Practice
- Challenges and Criticisms
- Case Studies
- Policy Implications
- The Future of Quota Rent
- Conclusion
What is Quota Rent?
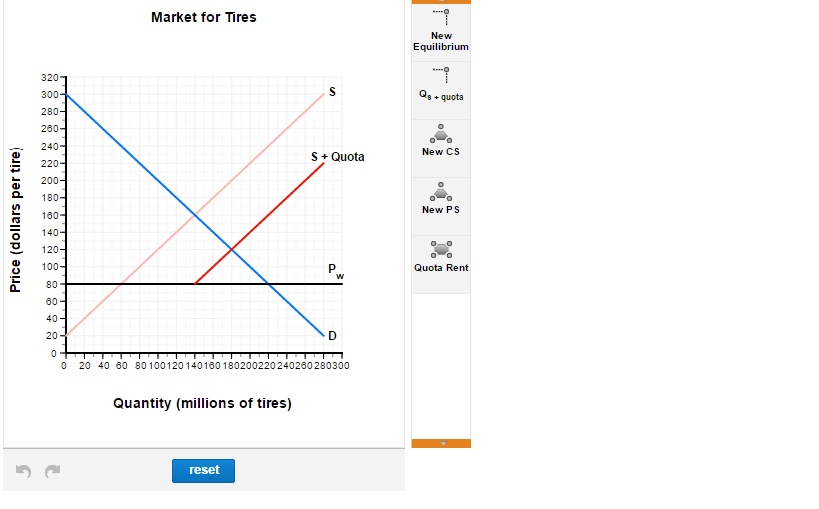
Quota rent refers to the economic benefit derived from the allocation of import or export quotas. These quotas limit the quantity of goods that can be traded across borders, creating artificial scarcity and driving up prices. The rent arises from the difference between the restricted quantity and the unrestricted market equilibrium.
Definition and Key Concepts
At its core, quota rent is the additional revenue generated by those who hold the rights to import or export goods under a quota system. This system can be implemented by governments to protect domestic industries, manage trade deficits, or achieve other policy objectives.
Key concepts to understand include:
- Import Quotas: Restrictions on the quantity of goods that can be imported into a country.
- Export Quotas: Limits on the quantity of goods that can be exported from a country.
- Quota Allocation: The process by which rights to trade under a quota are distributed.
Types of Quotas
Quotas come in various forms, each with its own characteristics and implications for quota rent. Understanding these types is essential for grasping how quota rent operates in different contexts.
1. Tariff Rate Quotas
Tariff rate quotas (TRQs) allow a specified quantity of goods to be imported at a reduced tariff rate, with higher tariffs applied to quantities exceeding the quota. This system creates a dual pricing structure, which can lead to significant quota rent for those holding allocation rights.
2. Absolute Quotas
Absolute quotas set a strict limit on the quantity of goods that can be traded. Once the quota is reached, no further imports or exports are allowed until the next quota period begins. This type of quota often results in high quota rent due to the scarcity it creates.
Read also:Aagmal Unlocking The Secrets Behind This Revolutionary Concept
Mechanisms of Quota Rent
The mechanisms through which quota rent is generated are rooted in the principles of supply and demand. By restricting the quantity of goods available in the market, quotas create artificial scarcity, driving up prices and generating rent for quota holders.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
When a quota is imposed, the supply curve shifts, leading to higher prices for consumers and increased profits for producers. This price differential represents the quota rent, which is captured by those who hold the rights to trade under the quota.
Quota Allocation Methods
Various methods are used to allocate quota rights, including auctions, administrative allocation, and grandfathering. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of efficiency, fairness, and the generation of quota rent.
Economic Impact of Quota Rent
The economic impact of quota rent is multifaceted, affecting consumers, producers, and governments in different ways. While quota rent can provide economic benefits to certain groups, it also has potential downsides that need to be carefully considered.
Consumer Impact
Consumers often face higher prices due to the artificial scarcity created by quotas. This can lead to reduced consumer surplus and decreased purchasing power. However, in some cases, quotas may protect domestic industries, leading to long-term benefits for consumers.
Producer Impact
Producers who hold quota rights can benefit significantly from the increased prices and profits generated by quota rent. This can lead to increased investment and innovation within the industry. However, it can also create inefficiencies if producers become overly reliant on quota protection.
Quota Rent in Practice
Quota rent is not just a theoretical concept; it has real-world applications that affect industries and economies around the globe. Examples can be found in various sectors, including agriculture, textiles, and manufacturing.
Agricultural Quotas
In the agricultural sector, quotas are often used to protect domestic farmers from international competition. This can lead to significant quota rent for farmers who hold allocation rights, but it can also result in higher food prices for consumers.
Textile Quotas
The textile industry has long been subject to quota systems, particularly in relation to trade between developed and developing countries. Quota rent in this sector can have significant implications for both producers and consumers.
Challenges and Criticisms
While quota rent can provide economic benefits, it is not without its challenges and criticisms. Policymakers must carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of quota systems to ensure they achieve their intended objectives.
Efficiency Concerns
Quotas can create inefficiencies in the market by distorting supply and demand dynamics. This can lead to reduced competition, higher prices, and decreased consumer welfare.
Fairness Issues
The allocation of quota rights can raise fairness concerns, particularly if the process is perceived as favoring certain groups over others. Transparent and equitable allocation methods are essential to maintaining public trust in quota systems.
Case Studies
Examining real-world examples of quota rent can provide valuable insights into its operation and impact. Case studies from different industries and regions highlight the diverse ways in which quota rent affects global trade.
Case Study 1: Sugar Quotas in the European Union
The European Union's sugar quota system has been a subject of debate for many years. By limiting the amount of sugar that can be produced and traded within the EU, the system generates significant quota rent for producers but also leads to higher prices for consumers.
Case Study 2: Textile Quotas in the United States
The United States has historically used textile quotas to protect its domestic industry from international competition. While this has generated quota rent for American producers, it has also led to criticism from trading partners and concerns about consumer welfare.
Policy Implications
The implementation of quota systems and the generation of quota rent have important policy implications for governments and international organizations. Policymakers must consider the broader economic, social, and political impacts of quota systems when designing trade policies.
Trade Negotiations
Quota systems are often a key issue in trade negotiations, as countries seek to balance their domestic interests with international obligations. Effective negotiation strategies are essential for achieving mutually beneficial outcomes.
Regulatory Frameworks
Developing robust regulatory frameworks for quota systems is crucial for ensuring their effectiveness and fairness. This includes establishing transparent allocation methods and monitoring compliance with quota limits.
The Future of Quota Rent
As global trade continues to evolve, the role of quota rent in shaping trade policies is likely to change. Emerging trends and challenges will require policymakers to adapt their approaches to ensure that quota systems remain relevant and effective.
Technological Advancements
Advances in technology may impact the way quota systems are implemented and monitored. Digital tools and platforms could enhance transparency and efficiency in quota allocation and management.
Global Trade Dynamics
Shifting global trade dynamics, including the rise of new economic powers and changing consumer preferences, will influence the future of quota rent. Policymakers must stay informed about these trends to make informed decisions about quota systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, quota rent is a complex and multifaceted concept that plays a significant role in shaping global trade policies. By understanding its mechanisms, impacts, and implications, policymakers, economists, and business leaders can make informed decisions about the use of quota systems.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and insights on this topic in the comments section below. Additionally, we invite you to explore other articles on our site for more in-depth analysis of global trade issues. Together, we can deepen our understanding of the forces shaping the global economy and work towards a more equitable and sustainable future.