Comprehensive RemoteIoT Web SSH Tutorial: Your Ultimate Guide
In today's digital age, remote access to IoT devices through web SSH has become increasingly vital for developers, administrators, and tech enthusiasts alike. Whether you're managing servers, monitoring IoT devices, or troubleshooting remotely, understanding how to use RemoteIoT web SSH effectively can significantly enhance your productivity and security. This tutorial will walk you through everything you need to know about setting up and using web SSH for remote IoT management.
As technology continues to evolve, remote IoT management has emerged as a critical component in modern IT infrastructure. With the rise of cloud computing and distributed systems, being able to securely access and control IoT devices from anywhere in the world is no longer a luxury but a necessity. This guide aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of RemoteIoT web SSH, its benefits, and step-by-step instructions for implementation.
Whether you're a beginner looking to learn the basics of web SSH or an experienced professional seeking advanced techniques, this tutorial is designed to cater to all levels of expertise. By the end of this article, you'll have the knowledge and tools necessary to confidently manage your IoT devices remotely.
Read also:Olivia Black Actress Rising Star In The Spotlight
Table of Contents:
- Biography (RemoteIoT Overview)
- Setting Up RemoteIoT Web SSH
- Security Best Practices for RemoteIoT Web SSH
- Tools and Software Requirements
- Establishing a Secure Connection
- Common SSH Commands for IoT Devices
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Optimizing RemoteIoT Web SSH Performance
- Automating Tasks with RemoteIoT Web SSH
- Future Trends in RemoteIoT Web SSH
RemoteIoT Overview
What is RemoteIoT?
RemoteIoT refers to the practice of managing and controlling Internet of Things (IoT) devices remotely. It enables administrators and developers to interact with IoT devices from anywhere in the world, provided they have an internet connection. This capability is particularly useful for monitoring and maintaining IoT networks, especially in large-scale deployments where physical access is not feasible.
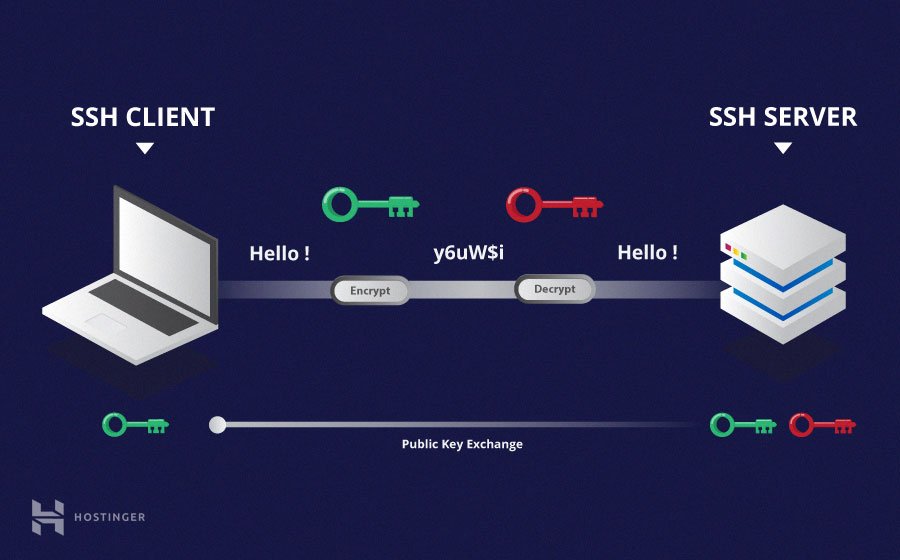
RemoteIoT systems typically use secure communication protocols such as SSH (Secure Shell) to ensure data integrity and confidentiality. Web SSH, in particular, allows users to access IoT devices via a web browser, eliminating the need for additional software installations.
Setting Up RemoteIoT Web SSH
Setting up RemoteIoT web SSH involves several key steps. Below is a detailed guide to help you get started:
Step 1: Install Necessary Software
- Install an SSH server on your IoT device. Popular options include OpenSSH and Dropbear.
- Ensure your IoT device has a stable internet connection.
- Set up a static IP address or dynamic DNS (DDNS) for easier access.
Step 2: Configure Firewall Settings
Adjust your firewall settings to allow incoming SSH connections. Be sure to use secure ports and restrict access to trusted IP addresses whenever possible.
Security Best Practices for RemoteIoT Web SSH
Security is paramount when using RemoteIoT web SSH. Here are some best practices to keep your IoT devices safe:
Read also:Charles Johnson Net Worth The Untold Story Of Success And Wealth
- Use strong, unique passwords or implement public key authentication.
- Disable root login to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regularly update your SSH server and IoT device firmware to protect against vulnerabilities.
Tools and Software Requirements
Several tools and software are essential for effective RemoteIoT web SSH management:
SSH Clients
- Putty: A popular SSH client for Windows users.
- Terminal: Built-in SSH client for macOS and Linux users.
- Web-based SSH clients: Such as ShellInABox and WebSSH2, which allow browser-based access.
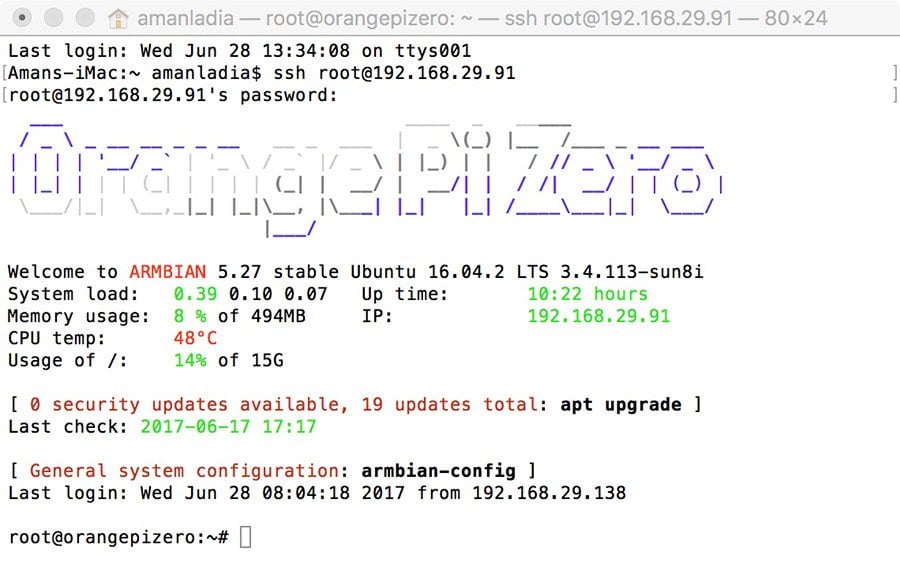
Establishing a Secure Connection
Connecting to your IoT device via web SSH involves the following steps:
- Open your preferred web-based SSH client in your browser.
- Enter the IP address or domain name of your IoT device.
- Input your login credentials and establish the connection.
Common SSH Commands for IoT Devices
Here are some frequently used SSH commands for managing IoT devices:
ls: List files and directories.cd: Change directory.sudo: Execute commands with superuser privileges.scp: Securely copy files between devices.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Encountering issues while using RemoteIoT web SSH is not uncommon. Below are some common problems and their solutions:
Connection Refused
If you receive a "Connection refused" error, ensure that:
- Your SSH server is running.
- The correct port is open in your firewall settings.
- Your IP address or domain name is accurate.
Optimizing RemoteIoT Web SSH Performance
To enhance the performance of your RemoteIoT web SSH setup, consider the following tips:
- Use compression to reduce data transfer size.
- Implement caching mechanisms for frequently accessed files.
- Upgrade your IoT device hardware if necessary to handle increased load.
Automating Tasks with RemoteIoT Web SSH
Automation can significantly streamline your RemoteIoT web SSH operations. Consider using tools like:
- Cron: Schedule repetitive tasks to run automatically.
- Ansible: Automate configuration management and deployment processes.
Future Trends in RemoteIoT Web SSH
As technology continues to advance, several trends are expected to shape the future of RemoteIoT web SSH:
- Quantum Computing: Potential advancements in encryption methods.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI-driven automation for enhanced security and efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, RemoteIoT web SSH is a powerful tool for managing IoT devices remotely. By following the steps outlined in this tutorial, you can set up a secure and efficient RemoteIoT web SSH system. Remember to prioritize security, leverage available tools, and stay updated with the latest trends to maximize your RemoteIoT capabilities.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into IoT and related technologies.
References: